Procurement 2.0 – a new perspective

New challenges
The economic crisis in 2008 forced companies to implement projects aimed at achievement of savings, as well as at other view on the function of procurement in enterprises. Many enterprises had to face the problem of cost reduction in order to maintain the financial liquidity as well as to prevent the negative effects of the crisis. These are the conditions in which management boards paid attention to the function of procurement as a source of generation of savings, which in straight line affect the financial results. However, the apparently simple task required the know-how and business competences to be successfully implemented. Attention was mainly paid to priorities of procurement in the context of the supply process implemented in the enterprise. The important issue was the economic efficiency of the implemented procurement projects performed through the search of savings associated with prices, as well as with the costs of the procurement process support. The main challenge became the selective approach to implementation of procurement, which in practice allowed to answer the question to what extent the relations with suppliers should be built, and to what extent one should focus mainly on prices. Although the traditional approach has ensured the stable process of supply, limited the risk associated with the production continuity, at the same time it has often shut the company off from new suppliers. Such a state of affairs results mainly from the supply policy, which was focused on identification and limitation of the risk in the supply chain. Cooperation with the closed group of verified suppliers obviously limits such a risk and, of course, there is nothing wrong with such an approach, assuming the selective approach to management of the procurement category, which comes down to the question where an added value of such an approach is, and in what kind of situations it is not efficient.
From marketing to procurement
For the first time, the above issue was highlighted by Kraljic, when publishing in 1983 the article containing the description of matrices, which allowed segmentation of procurement categories, as well as suppliers and techniques and tools used for implementation of procurement. Kraljic derived his concept from the marketing, which has been using many tools for segmentation of customers for a long time in order to adjust the product and communication with a market to the specific profiles of the customer. The main principle associated with the use of portfolio matrices is connected with the selective operation. Strategic products as well as bottlenecks are the typical categories in which the relations with suppliers play a significant role from the point of view of the efficient business. In such a case, the ongoing cooperation with a supplier, quality of products, service as well as the remaining added values define the success. In fact, the role of a procurement function comes down to the performance of activities, which safely can be described as relational negotiations. There is no room for threatening with competition and “forcing” the prices from the suppliers. The communication process in the procurement project should have a partnership nature. Also the involvement of the internal customer is important in order to build the value already at the stage of conduct of business talks. However, the left side of the Kraljic’s matrices requires the use of completely different type of tools and techniques, and mainly different competences. The lack of or small risks, as well as usually high degree of standardization enable the use of post-tender negotiations or electronic auctions which are focused on the competition on the supplier’s market and are aimed at the achievement of the assumed conditions of procurement.
Procurement and customers
The use of the marketing philosophy in procurement comes down also to taking into account the internal customers as well as the key stakeholders, the example of which is the following table:
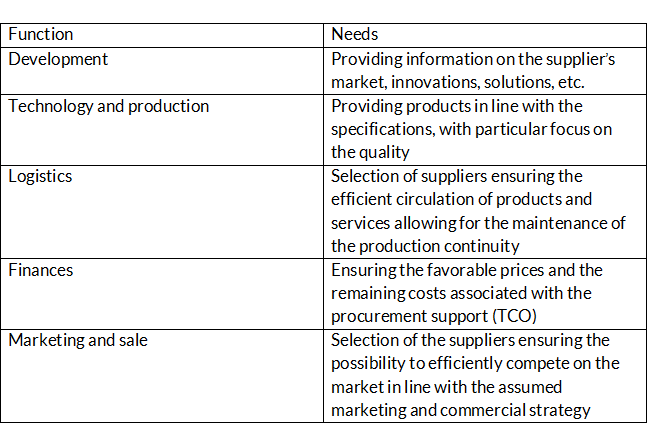
As it can be seen, efficient implementation of the function of procurement requires the cooperation at the strategic and tactical level with many key functions within organization. Procurement as a service function should be focused on assurance of the value required from the point of view of the internal customer. The problem in the practical implementation of the above assumptions is the occurrence of the natural conflict of objectives, which in particular concerns the financial, logistic and production function. However, the search for compromises between the various needs requires the enterprises to find the optimal solutions from the point of view of the entire business, and ultimately the final customer. Very good communication with customers and stakeholders is crucial for the entire procurement process, which in particular concerns the identification of the business needs understood as, among others, the required quality, cooperation conditions, securities in trade agreements, offered service, project management by the suppliers, provision of innovations, time of reaction to problems occurred during the cooperation. Complex procurement projects obviously require the involvement of people representing also other functions of the enterprise.
Strategy and tactics
The starting point in the discussion on strategic procurement is to define what such procurement is. On the one hand, we can assume that it means the implementation of procurement which are essential from the point of view of the enterprise; we can also refer to Kraljic’s matrices taking into account the risk of deliveries as well as the influence on the financial result or take into account the fact on which organization level such activities are implemented. An interesting reference point also seems to be the reference to the definition of the strategic management understood as the information and decision-making process focusing on the most important problems of the enterprise. In such a case, the strategic procurement is mainly the procurement strategy which is based on the analysis within this area. Under the procurement strategy, the following issues are addressed:
- Strategic purposes and initiatives
- Modeling and optimization of the organizational structure
- Management of the purchase category along with segmentation of suppliers
- Planning of human resources and competences necessary for implementation of the strategy
- Identification of the financial efforts necessary for implementation of the strategy
- Schedule of implementation of the objectives
- Identification of KPI for the procurement strategy
Therefore, the operational procurement will consist in the performance of the current tasks of the enterprise in line with the assumed procurement strategy, which means in particular the implementation of the following actions:
- The ongoing monitoring of the procurement needs of the enterprise
- Implementation of the procurement projects (RFI/RFP/RFQ, negotiations, e-auctions, formalisation of the cooperation)
- Monitoring of agreements concluded with the suppliers
- Analysis of the suppliers’ market (products, solutions, prices, trends)
- Reporting
- Ongoing communication with internal customers
To increase the efficiency of the procurement process as well as to correctly use the competences and potential of the team, it is important to separate the logistic tasks from the tasks requiring the involvement of merchants, which in particular concerns the tasks associated with initiation of deliveries (order) based on the concluded contracts and framework agreements.
Merchant’s competences
Other priorities of the logistics and purchases result in the need to develop completely different models of the desired competences on these two different positions. Of course, part of the competences will overlap, as for example the organizational abilities and analytical skills, however, it is worth to remember that the merchant is mainly a human for communication with the market responsible for usually rationale effect which results in the desired option for outputs. Such approach is, among others, very characteristic for merchants, whose work in fact come down to implementation of the designated targets. Ambitious approach to implementation of purposes, certain tendency to risk, knowledge on the psychology of behaviors, knowledge of not only negotiation techniques and procurement categories, but also the sale and marketing techniques used by the suppliers, will be the basis of success.
Earning money
Coming to the point, the modern approach to the purchase changes the way of thinking about this process from the typical supply to the search for the possibility to earn money through the search for savings. Of course, this type of actions are not only targeted to the conduct of tough negotiations with suppliers, but on the one hand are based on segmentation of categories, and on the other hand on the use of the savings leverage in relation to the categories where the relations with suppliers are not significantly important as well as in these where these relations determine the efficient cooperation with business partners. The example of such activities can be the optimization of not only product requirements, but also the contractual provisions as well as other values delivered by the suppliers. The already mentioned relational negotiations, taking into account the option win and win are the basis of implementation of purchases based on the relation. On other hand, opening up to the markets in categories subjected to low risk with simultaneous standardization of products may result in effective earning of money in procurement, more often called the generation of savings. Of course, there is also an issue concerning the calculation of such savings, not only in the context of prices, but also within the meaning of the value analysis, TCO, as well as in the translation into the result of the entire enterprise taking into account the incomes.
On-line
The efficient communication with the market requires the use of the modern IT technologies. Within 15-20 years, Google, Facebook, eBay, Allegro have been established. The e-commerce concept has been developed, which has facilitated procurement in B2C segment. However, not much has changed in this term in business procurement, except for the use of e-mail. After 2001, the horizontal and vertical marketplaces, which are used for communication between the merchants and sellers also in B2B segment, began to develop throughout the world. Also the private electronic markets and advanced software supporting the process of communication with suppliers have been established. It provided many enterprises with the possibility to create a window to the world at mutual benefits. At the same time, the process became simpler, more clear and faster. Of course, the basis of such a type of tools are still the strategical analysis of categories, which allow to achieve the response to which extent the electronic tools may be used at the given specifics of the enterprise.
Summary
In recent years, procurement has undergone a significant transformation, one of the reasons of which may be the increased interest of managers due to the need of orientation on the company costs. From the function integrated with the logistics, procurement has become an independent function, the basis of which is currently constituted also by psychology and marketing. At the same time, the management of not only the implementation of operational activities, but also the making of strategic decisions based on the advanced market analyses has been increased. Simultaneous popularization of the Internet favors the increase of efficiency within the scope of communication with the suppliers. Procurement, from the supply department, are becoming the structures bringing real values for the enterprise in many situations, allowing conversion into money. Where is this heading to? Certainly to separation and enhancement of procurement structures, higher competences, better decisions as well as even larger influence of procurement on the enterprise’s result.
